Complete Guide to the Low FODMAP Diet: Essential Tips for Success in 2025
The low FODMAP diet has garnered significant attention in recent years as a powerful approach to managing symptoms of IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) and improving gut health. By understanding what FODMAP foods are and how they affect digestion, individuals can effectively tailor their nutrition to reduce discomfort and enhance their overall well-being. This comprehensive guide will explore essential aspects of the low FODMAP diet, offering practical tips, delicious low FODMAP recipes, and helpful resources for success.
Understanding the Low FODMAP Diet
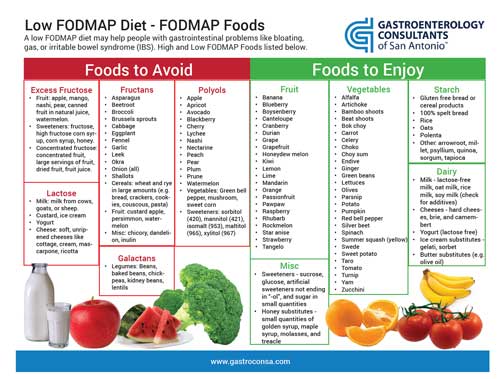
Before diving into the specifics, it’s crucial to grasp what a low FODMAP diet entails. FODMAP stands for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols – specific types of carbohydrates that can lead to digestive discomfort in some individuals. The diet aims to reduce these fermentable carbohydrates to alleviate gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating, gas, and abdominal pain, particularly among those suffering from IBS or food intolerances.
The FODMAP Definition: What to Know
The term FODMAP encompasses a variety of short-chain carbohydrates that should be minimized or avoided in your diet. Common high FODMAP foods include certain fruits like apples and pears, dairy products containing lactose, wheat-based products, and sweeteners containing sugar alcohols like sorbitol. By identifying and limiting these foods, individuals can greatly alleviate symptoms associated with digestive health issues. It’s essential to recognize that everyone’s tolerance to these foods can vary, which is why a consult with a dietitian can be beneficial when starting the diet.
Phases of the Low FODMAP Diet
The low FODMAP diet typically follows three phases: elimination, reintroduction, and personalization. The elimination phase involves avoiding high FODMAP foods for about 4 to 6 weeks. Following this phase, the reintroduction phase tests various FODMAP foods to determine the individual’s specific intolerances and tolerance levels. Finally, the personalization phase helps create a sustainable eating plan that incorporates low FODMAP and safe foods, tailored to each person’s digestion.
Benefits of the Low FODMAP Diet
One of the most significant health benefits of following a low FODMAP diet is the reduction of discomfort and symptoms related to IBS. Studies have shown that approximately 75% of patients report improved satisfaction with bowel function and a decrease in IBS symptoms when adhering to the diet. Additionally, focusing on low FODMAP foods encourages the inclusion of gut-friendly foods like lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables that enhance nutrient intake and support overall health.
Planning Your Low FODMAP Meals
Creating a successful low FODMAP meal plan involves understanding which foods fit into the diet. It’s helpful to have a structured approach to finding recipes that are low FODMAP and delicious, catering to all meal times, whether it’s breakfast, lunch, or dinner.
Low FODMAP Breakfast Ideas
Starting the day on a healthy note can be easy with the right low FODMAP breakfast options. Some fantastic ideas include oatmeal made with lactose-free milk, topped with strawberries or blueberries, and scrambled eggs served with spinach. Smoothies can also be a great way to provide essential nutrients; try blending spinach, kiwi, and lactose-free yogurt for a refreshing boost.
Creative Low FODMAP Lunch and Dinner Suggestions
Lunch and dinner can be equally satisfying with low FODMAP meals. For lunch, a quinoa salad with grilled chicken, cucumbers, and a drizzle of olive oil can be filling, while dinner options may include baked salmon with steamed carrots and potatoes. Emphasize using fresh herbs and spices for flavor and avoid high FODMAP sauces, opting for homemade alternatives that fit within low FODMAP cooking techniques.
Low FODMAP Snacks to Keep You Energized
Snacking can become challenging, but there are plenty of low FODMAP snacks that keep hunger at bay. Options such as rice cakes, popcorn, or lactose-free cheese with gluten-free crackers are excellent choices. Alternatively, consider preparations like low FODMAP homemade energy balls made from peanut butter and oats or a handful of macadamia nuts, which are also gut-friendly.
Low FODMAP Cooking Tips
Successful navigation of the low FODMAP diet is not just about avoiding high FODMAP foods but also about incorporating safe options in delicious ways. Here are some cooking tips that will enhance the flavor and nutritional value of your meals.
Understanding Low FODMAP Substitutions
When it comes to low FODMAP substitutions, creativity is key. For instance, instead of traditional pasta which contains wheat, opt for low FODMAP pasta alternatives like rice or quinoa-based options. For baking, consider using almond flour instead of traditional wheat flour to accommodate wheat intolerances. These adjustments ensure you can still enjoy your favorite dishes while adhering to the low FODMAP diet.
Meal Prep for Success
Meal prep can be an invaluable strategy when following a low FODMAP meal plan. Prepare dishes in advance and store them in individual servings to make it easy to grab meals throughout the week. Consider cooking batches of suitable grains like quinoa or rice, grilling proteins, and roasting vegetables ahead of time. This practice not only saves time but also reduces the temptation to resort to high FODMAP convenience foods.
Exploring Low FODMAP Desserts
Satisfying your sweet tooth doesn’t have to be daunting on a low FODMAP diet. There are many low FODMAP dessert recipes that incorporate safe ingredients like lactose-free dairy, coconut cream, or dark chocolate in moderation. For instance, you can make a low FODMAP chocolate avocado mousse or lactose-free almond cake for a scrumptious treat without the discomfort.
Frequently Asked Questions on the Low FODMAP Diet
This section aims to address some common queries surrounding the “low FODMAP diet,” elucidating potential pitfalls and tips for success.
1. Can I drink alcohol on the low FODMAP diet?
While some alcoholic beverages, like spirits and low FODMAP cocktails, are usually acceptable, drinks that contain high FODMAP mixers should be avoided. Be cautious with wine, as certain varieties may contain sulfites, which can trigger digestive discomfort in some individuals.
2. Can children follow a low FODMAP diet?
Yes, children can follow a low FODMAP diet, but it’s crucial to ensure they receive adequate nutrition. Consulting a dietitian can provide guidance on appropriate options and meals to maintain dietary balance while adhering to FODMAP guidelines.
3. How can I make eating out easier on a low FODMAP diet?
Dining out while on a low FODMAP diet can be challenging, but many restaurants are becoming more accommodating. Review the menu in advance, and don’t hesitate to speak to staff about dietary concerns. Look for restaurants that offer low FODMAP-friendly options or those that provide alternative gluten-free and lactose-free ingredients.
4. Is the low FODMAP diet suitable for everyone?
No, the low FODMAP diet is primarily designed for those suffering from IBS and related digestive health conditions. Individuals should approach the diet under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure optimal results based on their specific needs.
5. How long should I stay on the low FODMAP diet?
The low FODMAP diet should generally be followed for 4 to 6 weeks during the elimination phase. The next phase involves reintroducing foods to identify safe food choices while creating a maintenance diet that is both nutritious and manageable.
6. What resources are available for new low FODMAP dieters?
Numerous resources exist for those new to the low FODMAP diet. Websites, cookbooks, and mobile apps designed specifically for the diet can guide you in food shopping, meal prepping, and recipe formulations. Additionally, professional dietitian services can aid in effective dietary management.
7. How can the low FODMAP diet support my gut health?
The low FODMAP diet works by reducing the intake of specific fermentable carbohydrates that may exacerbate IBS symptoms and others’ gut discomfort. Adopting a healthy, balanced diet featuring low FODMAP foods supports digestive health and can promote a balanced gut microbiome.
By thoroughly understanding the low FODMAP principles, planning, exploring, and embracing this approach, you’re well on your way to achieving a happier gut and better living. Enjoy experimenting with low FODMAP recipes, and don’t hesitate to reach out to the low FODMAP community for support during your dietary journey!