Coyote Diet: Understanding Feeding Habits for Improved Wildlife Management in 2025
Coyote Feeding Habits
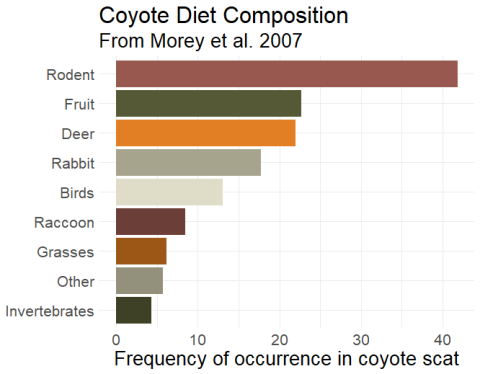
Coyotes are highly adaptable predators whose **feeding habits** can vary significantly based on seasonal changes, geographic location, and availability of food. Understanding coyote diets is crucial for wildlife management efforts, especially in regions experiencing shifts in their ecological balance. Their diet primarily consists of small mammals, including **rodents**, birds, and even insects, but they are opportunistic feeders, incorporating both plant and animal matter into their diet. This article explores various aspects of coyote feeding behavior, highlighting their diverse food sources and nutritional needs.
Coyote Food Sources
The **food sources** of coyotes can broadly be divided into two categories: animal-based and plant-based. While small mammals like rabbits and **rodents** are primary prey, coyotes also scavenge and consume carrion when available. Additionally, their **plant diet** can include berries, fruits, and various vegetation. This omnivorous versatility allows them to thrive in both **urban** and **rural environments** by adjusting their diets according to the resources at hand. Enhanced understanding of these **food preferences** aids in developing strategies that cater to wildlife populations, ensuring coyote sustainability without negatively impacting larger ecosystems.
Coyote Nutrition and Dietary Needs
Coyotes require a varied diet to meet their **nutritional needs**, which include proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Their primary **meat consumption** is significant when obtaining these nutrients, especially during breeding seasons when energy requirements increase. Efficient foraging strategies are crucial for finding optimal food sources, helping them maintain a healthy body weight and support their overall health. Identifying key aspects of coyote nutrition supports wildlife conservation by helping manage their ecosystems effectively.
Coyote Scavenging and Foraging Behavior
Coyotes exhibit unique **foraging behavior**, often returning to areas where food sources are reliably abundant. Their scavenging nature also plays a vital role in local ecosystems, as they help with the cleanup of carrion and dead wildlife, preventing the spread of disease. Understanding their **scavenging** and **hunting** methods helps researchers monitor their population dynamics while managing the potential impacts on prey species. Recognizing interaction dynamics among coyotes and other local wildlife is essential for informed wildlife management practices.
Coyote Prey and Dietary Competition
The balance of predator and prey is central to the ecological framework where coyotes reside. Their unique role as versatile predators grants them access to a diverse array of food sources, but it can lead to competition with other predators. Understanding coyote **predation patterns** provides insights into their ecological importance and influence on prey populations. Furthermore, local **dietary competition** affects their behavioral ecology, emphasizing the need for data-driven wildlife management methods in both urban and rural areas.
Coyote Impact on Small Mammals
Coyotes can have significant effects on small mammal populations, playing a role in regulating species dynamics. Understanding the **coyote impact** on species like rabbits and **rodents** helps wildlife biologists analyze changes in population health and biodiversity in different habitats. By conducting research regarding the interplay between coyotes and their prey, managers can guide practices aimed at maintaining equilibrium within ecosystems.
Urban vs. Rural Coyote Diet
The **coyote urban diet** can diverge significantly from that of its rural counterpart. Urban coyotes often exhibit more opportunistic feeding habits, consuming refuse, pet food, and various human-related waste. In contrast, their rural counterparts rely on wild prey, predominantly small mammals. By analyzing these different diets, researchers can develop urban wildlife **management strategies** that mitigate conflicts between coyotes and human populations while preserving the ecological roles of these predators.
Coyote Seasonal Changes and Dietary Adaptations
As seasons change, so do coyote diets. During winter months, availability of **food sources** shifts, leading to distinct **seasonal changes** in their feeding behavior. The abundance of certain prey can dictate how coyotes adapt their hunting and foraging methods. Acknowledging these adaptations can significantly aid wildlife management and inform policy adjustments necessary for preserving the delicate balance within environments these animals inhabit.
Understanding Coyote Health Through Diet
Exploring the relationship between **coyote health** and their feeding patterns reveals insights into their well-being and population dynamics. Healthy diets correlate with strong reproductive success and population vigor. Coyote **weight management** is also influenced by available resources, making it essential to monitor food availability for sustaining healthy communities of these adaptable predators.
Coyote Eating Behavior and Reproduction
The **eating behavior** of coyotes not only influences their health but also plays a pivotal role in their **reproduction**. A well-nourished coyote population demonstrates higher survival rates in offspring, directly linking diet to success in breeding. An investigative approach toward understanding the dynamics between reproduction and feeding habits can bolster wildlife conservation efforts and inform management practices that promote thriving coyote populations.
Coyote Digestive System and Food Selection
Coyotes possess a highly adaptive digestive system that allows them to process various food sources efficiently. Their **food selection** is guided by availability and nutritional content, emphasizing the significance of understanding how their bodies utilize different types of food. Ongoing research into their **digestive system** assists in gauging the health and adaptability of coyote populations amidst changing environmental conditions.
Conclusion: Improving Coyote Resource Management
Understanding the coyote diet, their feeding habits, and their role in ecosystems is crucial for effective **wildlife management** strategies moving forward. Insight into coyote food sources leads to informed practices that enhance both species conservation and ecological balance. In 2025 and beyond, continued research and exploration of innovative management approaches will help ensure the longevity of both coyotes and the environments they inhabit.
FAQ
1. What are the primary components of a coyote’s diet?
A coyote’s diet mainly consists of small mammals such as **rodents** and rabbits, along with birds, insects, and plants like berries. They are opportunistic feeders, adapting their diet based on available food sources, including **carrion** and human refuse in urban areas.
2. How does the coyote diet differ in urban and rural environments?
Urban coyotes often consume human-related waste and pet food, whereas rural coyotes primarily hunt local prey such as rabbits and **rodents**. These behavioral adaptations influence how they coexist with humans and maintain ecological roles.
3. Do coyotes play a significant role in their ecosystems?
Yes, coyotes are pivotal in controlling small mammal populations and contributing to the health of the ecosystem. Their predation helps balance species dynamics, influencing biodiversity and resource management practices in their habitats.
4. What impact does seasonal change have on coyote feeding habits?
Seasonal variations significantly influence the **food availability**, leading coyotes to adapt their foraging strategies. For instance, during winter, they may rely more heavily on alternative food sources as their primary prey becomes scarcer.
5. How can wildlife management practices help sustain coyote populations?
Effective wildlife management requires understanding coyote diets and ensuring environmental conditions support a balanced ecosystem. Strategies such as monitoring food availability and minimizing conflicts with humans can foster coexistence and health within coyote communities.
6. What are some common health issues related to poor coyote diets?
Poor diets can lead to various health issues in coyotes, including malnutrition and long-term health problems affecting reproduction and survival. Monitoring local food sources and ensuring their nutrient balance can aid in maintaining healthy populations.
7. How do coyotes compete with other predators for food?
Coyotes often share their habitat with other predators and may experience competition for food, particularly in densely populated areas. Understanding these dynamics can inform management practices aimed at maintaining ecological balance and promoting biodiversity.